SimpleHeadphoneIR: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:SimpleHeadphoneIR-0.1.png|right|thumb|225px]] |
[[File:SimpleHeadphoneIR-0.1.png|right|thumb|225px]] |
||
In conventions SimpleHeadphoneIR we store IRs of the system headphone-ear, i.e. headphone IRs. The most important properties of SimpleHeadphoneIR are: |
|||
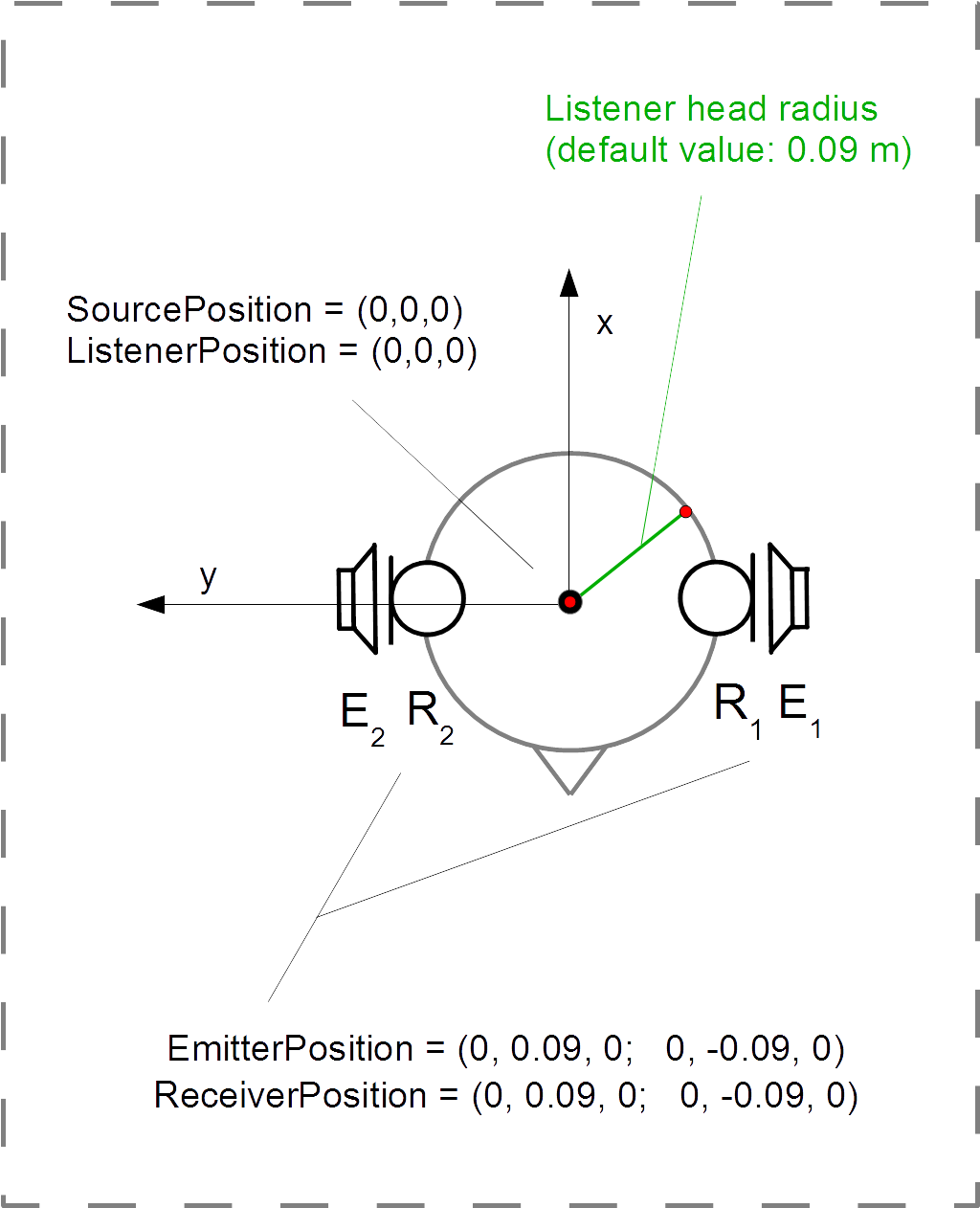
* '''One-to-one correspondence between emitters and receivers''': When measuring headphones, we usually have two headphones (=two emitters, E1 and E2) and we have two mics places in the ears (=two receivers, R1 and R2). For the first measurement: E1-->R1,R2; next measurement: E2-->R1, R2. Usually, the IRs E1-->R1 and E2-->R2 are the interesting IRs and are usually further processed. This one-to-one correspondence of emitters and receivers is a strict property of SimpleHeadphoneIR. (If you also need the crosstalk IRs, i.e., E1-->R2 and E2-->R1, GeneralFIR is recommended). |
|||
* '''Single listener''': in a single file, IRs of a single listener are stored. Note that multiple measurements of the same listener can still be stored in a single file. |
|||
* '''Simple sources, simple listeners''': the orientation (View and Up variables) of the emitters and receivers are not considered. This makes the conventions simple, corresponding to the simplicity of SimpleFreeFieldHRIR. |
|||
== Proposed version 0.1 == |
== Proposed version 0.1 == |
||
Revision as of 09:18, 23 July 2014
Conventions for IRs with a 1-to-1 correspondence between emitter and receiver. The main application for this convention is to store headphone IRs recorded for each emitter and each ear.
Proposed version 0.1
In conventions SimpleHeadphoneIR we store IRs of the system headphone-ear, i.e. headphone IRs. The most important properties of SimpleHeadphoneIR are:
- One-to-one correspondence between emitters and receivers: When measuring headphones, we usually have two headphones (=two emitters, E1 and E2) and we have two mics places in the ears (=two receivers, R1 and R2). For the first measurement: E1-->R1,R2; next measurement: E2-->R1, R2. Usually, the IRs E1-->R1 and E2-->R2 are the interesting IRs and are usually further processed. This one-to-one correspondence of emitters and receivers is a strict property of SimpleHeadphoneIR. (If you also need the crosstalk IRs, i.e., E1-->R2 and E2-->R1, GeneralFIR is recommended).
- Single listener: in a single file, IRs of a single listener are stored. Note that multiple measurements of the same listener can still be stored in a single file.
- Simple sources, simple listeners: the orientation (View and Up variables) of the emitters and receivers are not considered. This makes the conventions simple, corresponding to the simplicity of SimpleFreeFieldHRIR.
Proposed version 0.1
This conventions proposal is deprecated - a new proposal is currently under development. Contribute by discussing with us (use the "Discussion" tab).
| Name | Default | Flags | Dimensions | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLOBAL:Conventions | SOFA | rm | attribute | ||
| GLOBAL:Version | 0.5 | rm | attribute | ||
| GLOBAL:SOFAConventions | HeadphoneIR | rm | attribute | Conventions for IRs with a 1-to-1 correspondence between emitter and receiver. The main application for this convention is to store headphone IRs recorded for each emitter and each ear. | |
| GLOBAL:SOFAConventionsVersion | 0.1 | rm | attribute | ||
| GLOBAL:APIName | rm | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:APIVersion | rm | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:ApplicationName | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:ApplicationVersion | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:AuthorContact | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:Comment | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:DataType | FIR | rm | attribute | We will store IRs here | |
| GLOBAL:History | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:License | No license provided, ask the author for permission | m | attribute | ||
| GLOBAL:Organization | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:References | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:RoomType | free field | m | attribute | Room type is not relevant here | |
| GLOBAL:Source | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:TimeCreated | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:TimeModified | m | attribute | |||
| GLOBAL:Title | m | attribute | |||
| ListenerPosition | [0 0 0] | m | IC, MC | double | |
| ListenerPosition:Type | cartesian | m | attribute | ||
| ListenerPosition:Units | meter | m | attribute | ||
| ReceiverPosition | [0 -0.09 0; 0 0.09 0] | m | rCI, rCM | double | |
| ReceiverPosition:Type | cartesian | m | attribute | ||
| ReceiverPosition:Units | meter | m | attribute | ||
| SourcePosition | [0 0 0] | m | IC, MC | double | Headphones are located at the position of the listener |
| SourcePosition:Type | spherical | m | attribute | ||
| SourcePosition:Units | degree, degree, meter | m | attribute | ||
| EmitterPosition | [0 -0.09 0; 0 0.09 0] | m | eCI, eCM | double | Reflects the correspondence of each emitter to each receiver |
| EmitterPosition:Type | cartesian | m | attribute | ||
| EmitterPosition:Units | meter | m | attribute | ||
| GLOBAL:DatabaseName | m | attribute | to which HRTF database these data correspond? | ||
| GLOBAL:SubjectID | m | attribute | to which subject from the database these data correspond? | ||
| GLOBAL:SourceProducer | attribute | who produced the headphones? | |||
| GLOBAL:SourceModel | attribute | how is this headphone called? | |||
| GLOBAL:ProcessingState | attribute | how are the IRs processed (raw, equalized, etc)? | |||
| GLOBAL:ListenerDescription | attribute | describe the listener here (human, dummy head, etc) | |||
| GLOBAL:SourceDescription | attribute | describe the headphones here | |||
| GLOBAL:ReceiverDescription | attribute | describe the microphones here | |||
| GLOBAL:EmitterDescription | attribute | describe the drivers of the headphones here | |||
| Data.IR | [1 1] | m | mRn | double | |
| Data.SamplingRate | 48000 | m | I | double | |
| Data.SamplingRate:Units | hertz | m | attribute | ||
| Data.Delay | [0 0] | m | IR, MR | double |